Commercial invoice
As a product supplier, you can upload the commercial invoice directly in LRP Proveedores, within the Shipments module.
The commercial invoice is uploaded at the shipment level, since it corresponds to the products shipped in a specific shipment.
Registering the commercial invoice at the shipment level allows the customer to access the final shipment information required for logistics, customs, and cost processes.
The following steps explain how to upload a commercial invoice within the platform.
How to upload a commercial invoice to a shipment
Go to Shipments from the main menu.
In this view, you will see all shipments associated with the purchase orders that include the shipped products.In the Actions column, click the Edit icon of the shipment you want to manage to open its detail view.
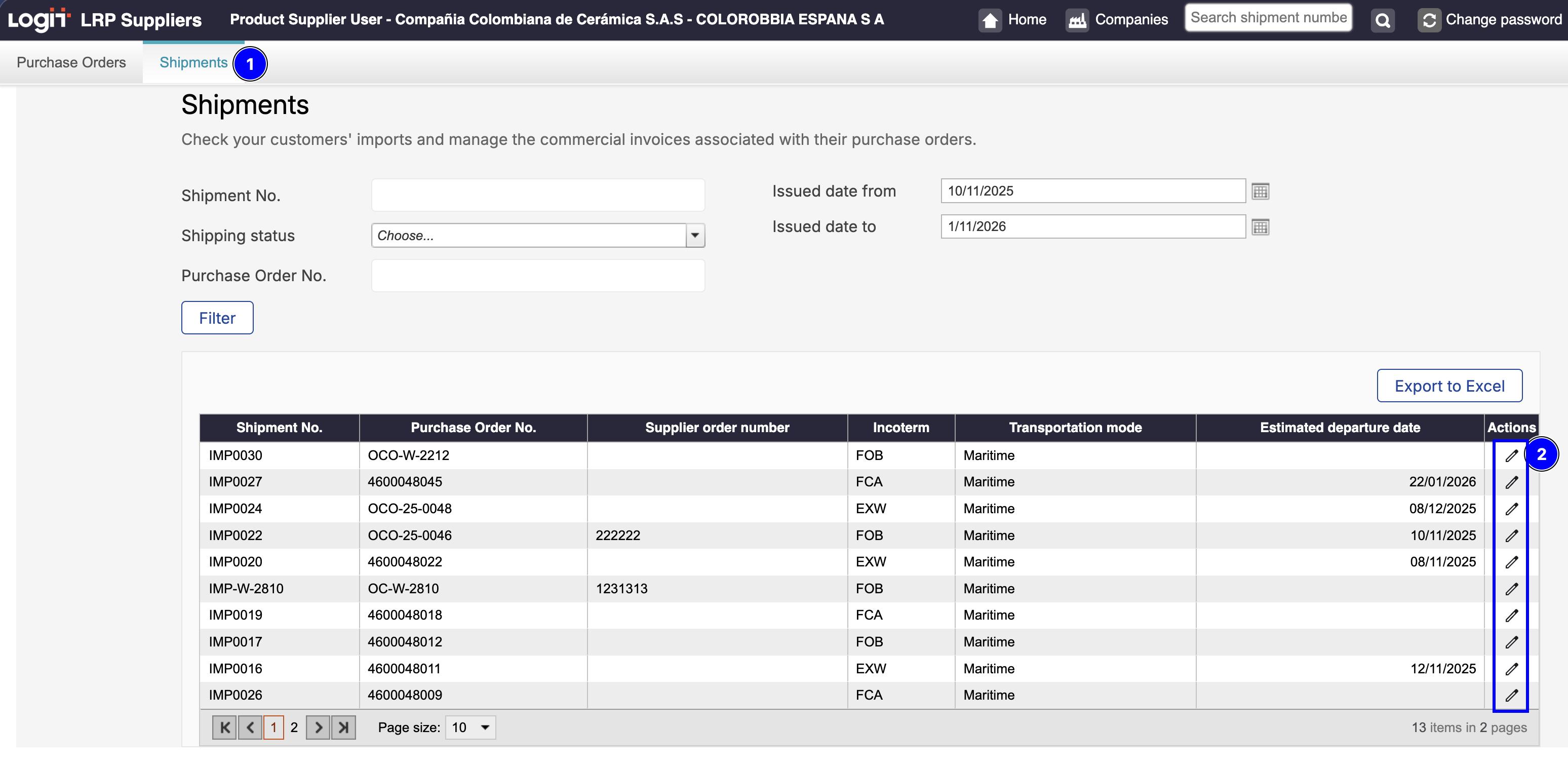
Edit a Shiptment
In the shipment detail screen, you will see a table with the shipped products.
To add a commercial invoice, click Upload invoices.
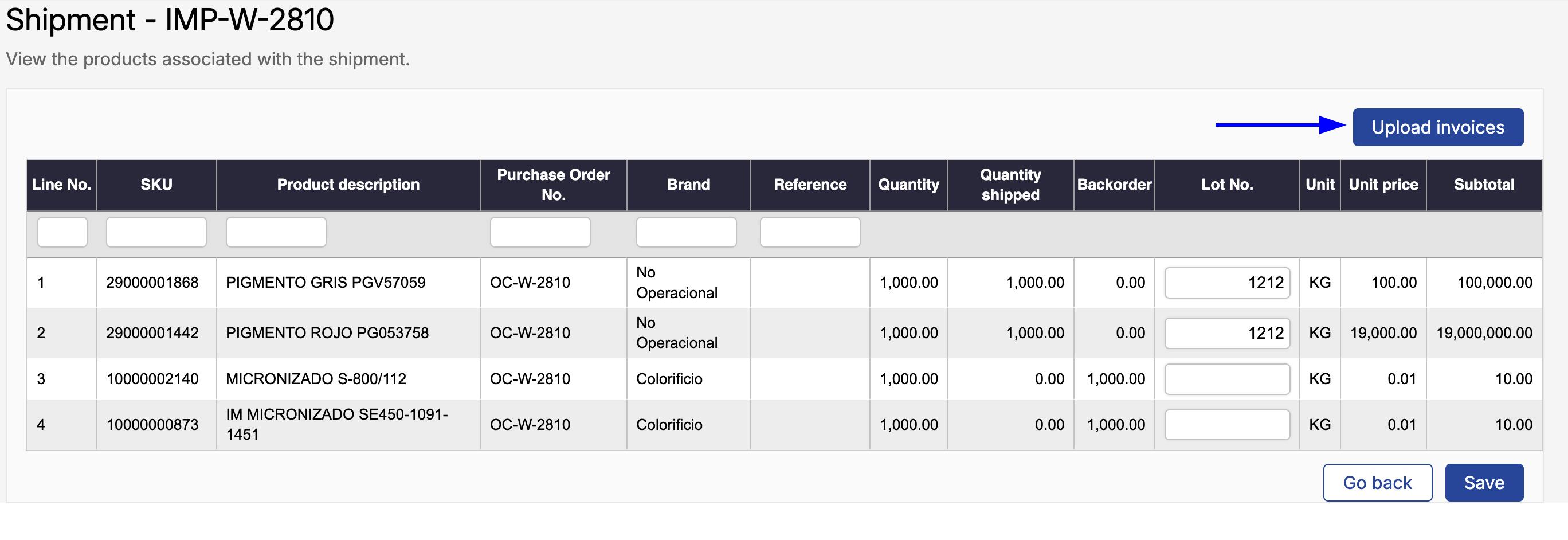
Upload invoices action
A new window will open showing the Commercial documents already registered for the selected shipment.
Click New document.
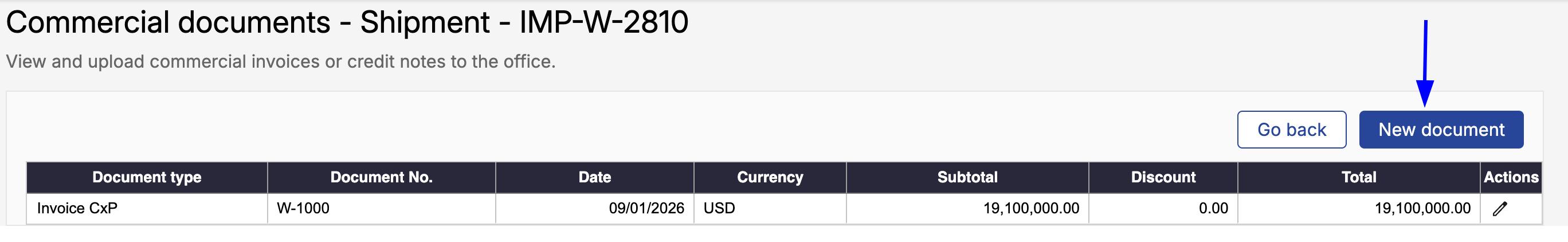
Select the document type Commercial Invoice and complete the required information.
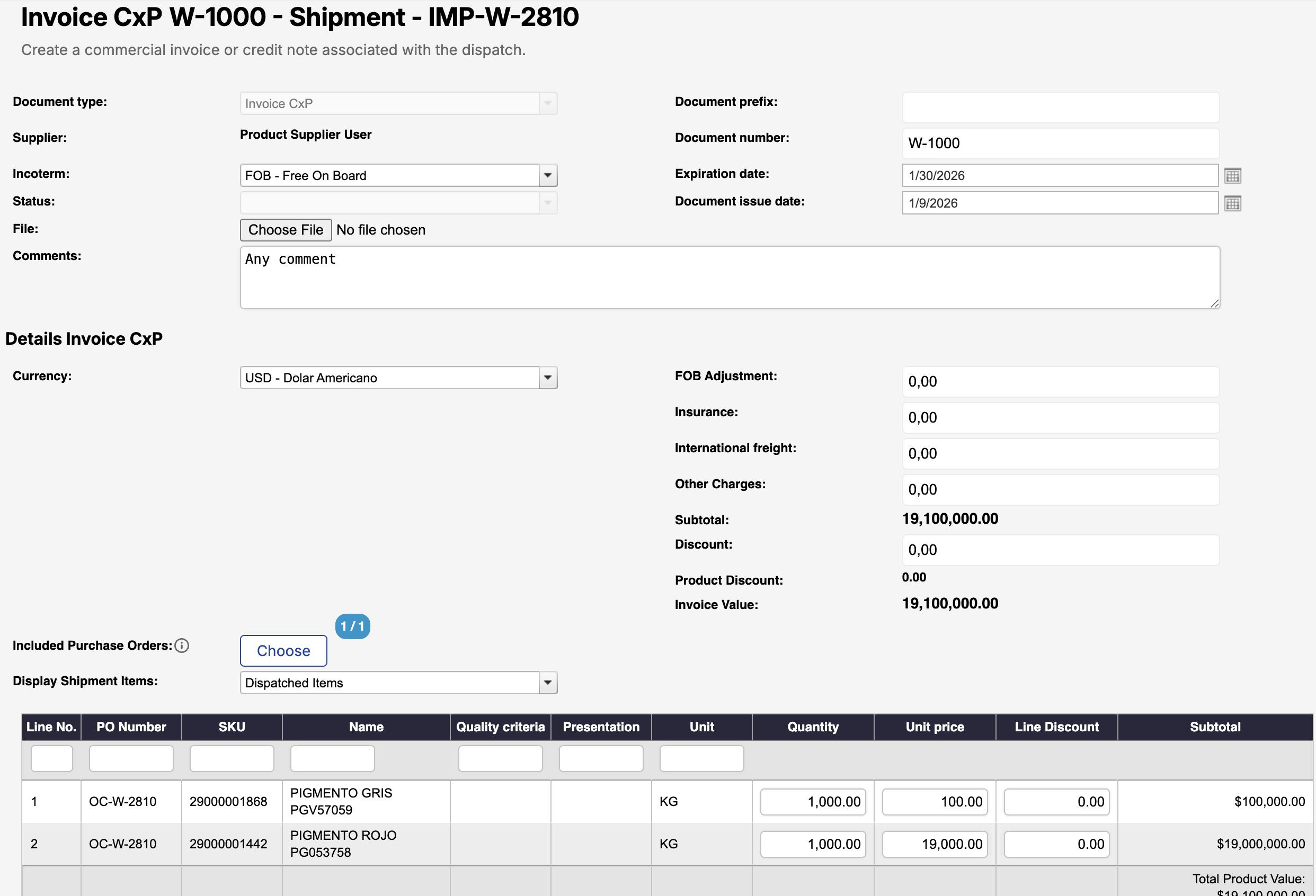
Click Save to finish.
Once uploaded, the commercial invoice will be associated with the shipment and will be available to the client for their logistics, customs, and cost processes.
Read the definitions below and identify which information is required.
Commercial Invoice – Field definitions
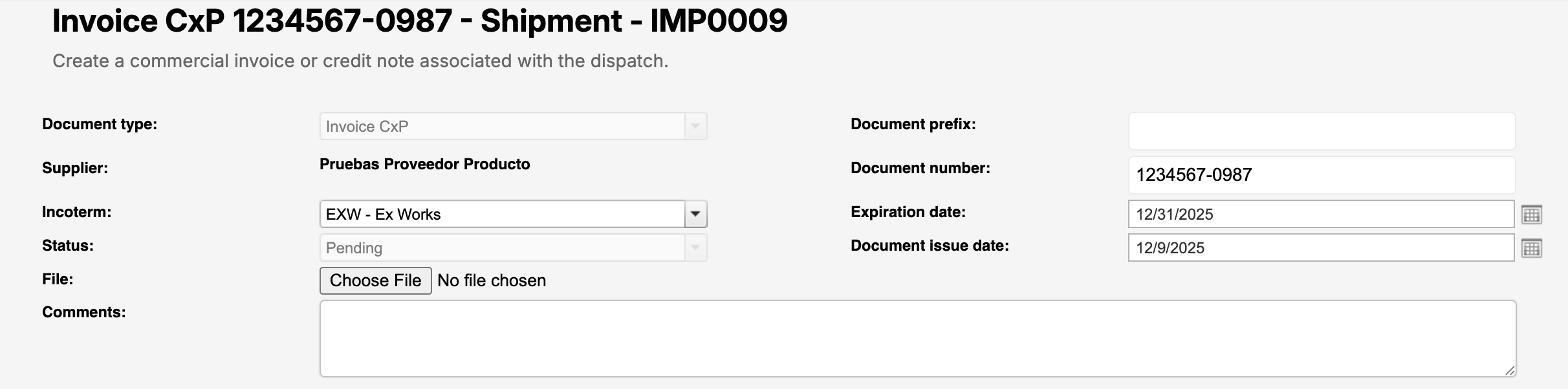
Document type: Defines the type of commercial document: Invoice CxP (Commercial Invoice) in this case.
Supplier: Displays the supplier associated with the shipment.
Pre-filled and not editable.Incoterm (Required): Indicates the Incoterm under which the goods are sold.
Status: Shows the current status of the document (e.g., Pending).
File: Allows you to upload the commercial invoice file (PDF or supported format).
The uploaded file represents the official commercial invoice document.Comments: Optional field to add notes or clarifications related to the invoice.
Document prefix: Optional prefix used as part of the document reference, if applicable.
Document number (Required): The official commercial invoice number issued by the supplier.
This number must match the uploaded document.Document issue date: The date on which the commercial invoice was issued.
Expiration date (Required): Indicates the validity or expiration date of the invoice, when applicable.
Required for customs and compliance purposes.
Details – Invoice CxP
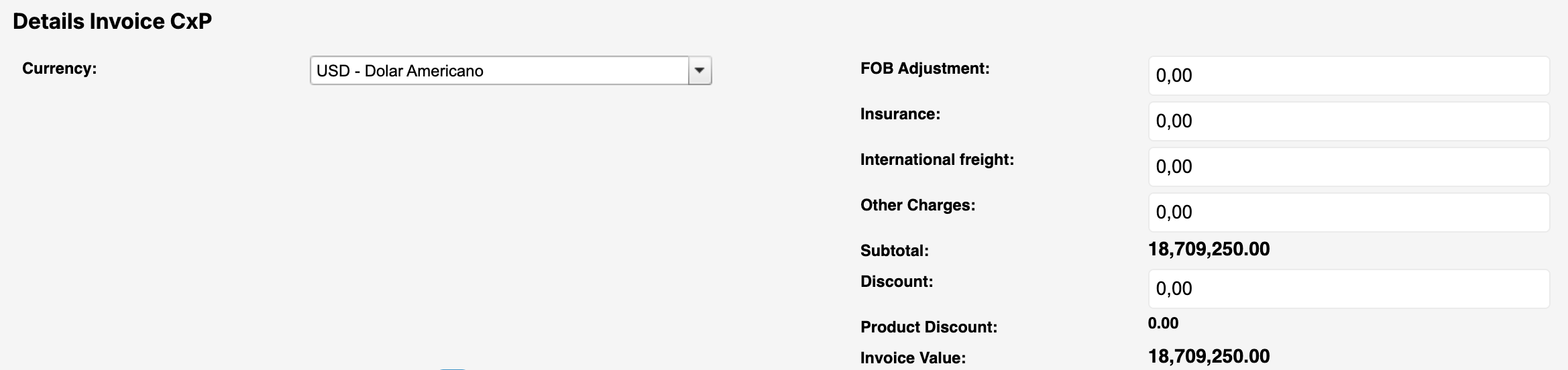
Currency (Required): The currency in which the commercial invoice is issued.
FOB Adjustment (Optional):
This field is used when the commercial invoice is not issued with a FOB value.
It allows adjusting the FOB amount by separating insurance, international freight, and other applicable costs, so that the shipment values are properly reflected during the final settlement and customs processes.
Examples (click to expand).
Insurance (Optional): The insurance cost associated with the shipment.
This value is relevant for customs valuation and is typically required when the Incoterm includes insurance coverage.International freight (Optional): The cost of international transportation from origin to destination.
Depending on the Incoterm, this value may be included or excluded from the invoice total.Other Charges (Optional): Additional costs related to the shipment that are not covered by freight or insurance, such as handling fees or special services.
Subtotal (Calculated / Read-only): The total value of the goods before discounts and additional charges.
This field is usually calculated based on the invoice line items and cannot be edited manually.Discount (Optional): A general discount applied to the invoice total.
This discount affects the overall invoice value and must be aligned with the commercial agreement.Product Discount (calculated / read-only): Discounts applied specifically at the product level (line discount in the table bellow).
Invoice Value (Calculated / Read-only): The final total value of the invoice after applying discounts, adjustments, freight, insurance, and other charges.
This is the amount used for financial and customs processes.
Table fields definitions
By default, the table is prefilled with the quantities dispatched for each product.
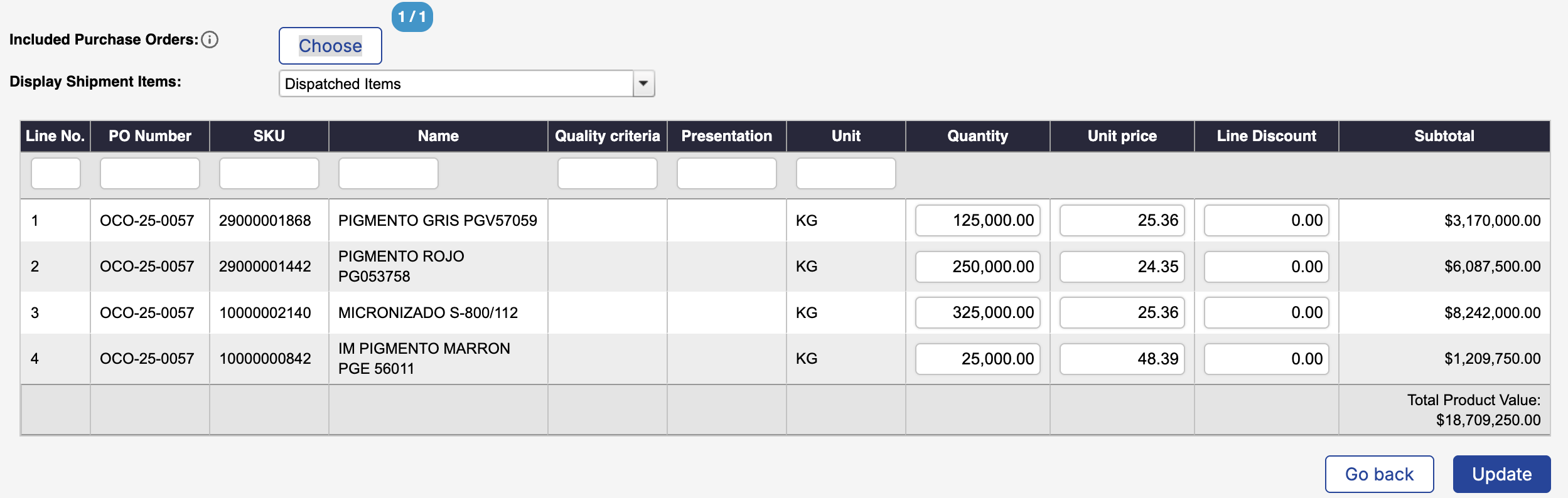
You can filter the table using the text fields displayed below each column header.
Filtering does not affect the data you enter: when you save, all values you have entered will be preserved, even if some rows are filtered out at the moment of saving.
Included purchase orders: Filters the table by the purchase orders associated with the shipment.
Display Shipment Items: By default, this option shows only the items that have been dispatched in the shipment.
You can also switch the filter to display all items included in the purchase orders associated with the shipment.Dispatched Items – Items already dispatched in the shipment.
All Items – All items from the purchase orders associated with the shipment.
Line No.: Used to identify the position of each product within the table. For companies with system integrations, this field is also used to maintain data consistency across systems.
Purchase Order No.: Indicates the purchase order to which the SKU belongs.
SKU: The product reference code (Stock Keeping Unit) used to uniquely identify each product.
Product description (Commercial name): The commercial name assigned to the product when it is created. This field can also be used to filter the table and quickly locate products.
Quality criteria: Some companies use additional criteria, beyond the SKU, to further describe a product. For example, color variations for products that share the same SKU.
Presentation: Describes how the product is packaged or presented for sale or transportation, depending on the case. For example, textiles may have a presentation such as “roll”.
Unit: Indicates the unit of measure used to count or weigh the product. Units may vary depending on the product type and can include kg, unit (u), package, etc.
Quantity: The quantity used for invoice calculations.
Unit price: Represents the price of a single unit of the product, expressed in the corresponding currency (e.g., USD, EUR).
Subtotal: Represents the total cost for each product line. The subtotal is calculated by multiplying the unit price by the quantity.
This value reflects the gross cost per line item, before applying any discounts, taxes, or additional charges at the invoice level.
